Price elasticity of demand is classified under the following five subheads:
a) Perfectly elastic demand: It refers to the situation where the slightest rise in price causes, the quantity demanded of a commodity to fall to zero and at the the present level of price people demand an infinitely large quantity of the commodity. The coefficient of elasticity of demand is infinite.
![]()
Fig: Perfectly elastic demand
b) Perfectly inelastic demand: It refers to the situation where even substantial changes in price do not make any change in the quantity demanded, i.e., for any change in the price, the demand remains constant. The coefficient of elasticity of demand is zero.
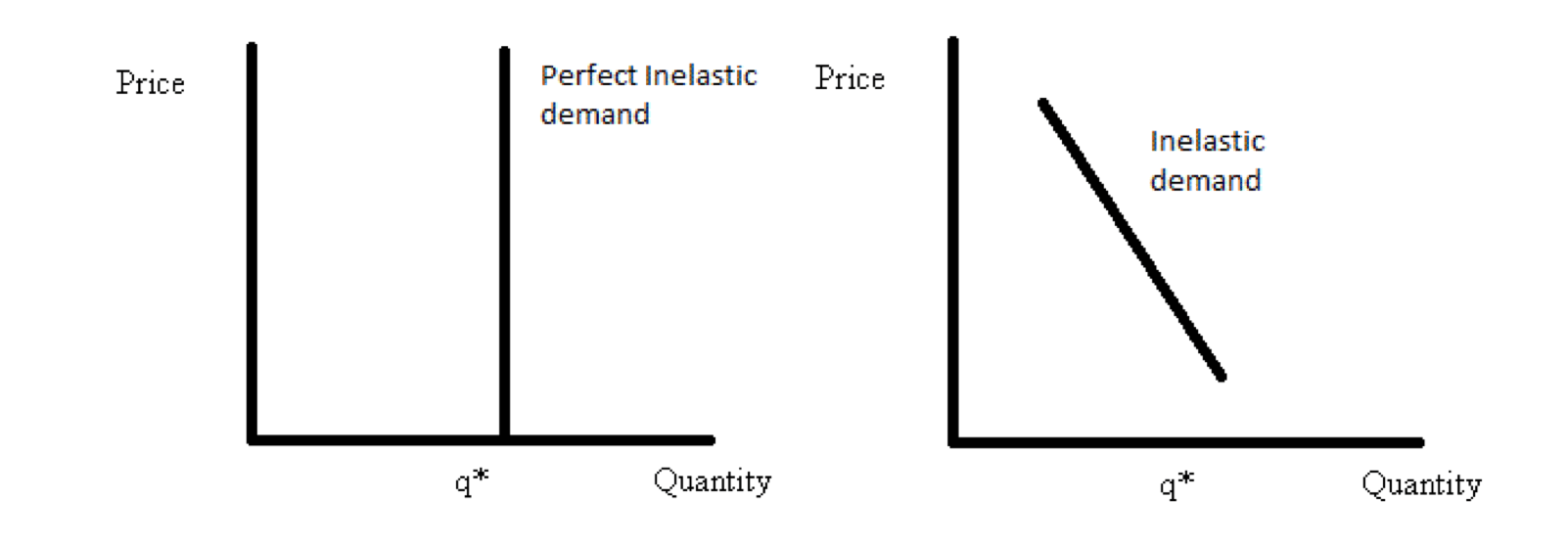
Fig: Perfectly inelastic demand
c) Relatively elastic demand: Here, a small proportionate change in the price of commodity results in a larger proportionate change in its quantity demanded. The coefficient of elasticity of demand is greater than unity.
Fig: Relatively elastic demand
d) Relatively Inelastic demand: A larger proportionate change in the price of a commodity results in a smaller proportionate change in its quantity demanded. The coefficient of elasticity of demand is greater than zero but less than unity.
Fig: Relatively inelastic demand
e) Unitary elastic demand: It refers to a situation where a given proportionate change in price is accompanied by an equally proportionate change in the quantity demanded. In other words, a given proportionate fall in the price is followed by an equally proportionate increase in demand and vice versa. The coefficient of elasticity of demand is unity.

Fig: Unitary elastic demand
