Income elasticity of demand can be divided into the following five sub-heads:
a) Zero income elasticity: A given increase in the consumer’s money income does not result in an increase in the quantity demanded of a commodity (Ei=0).
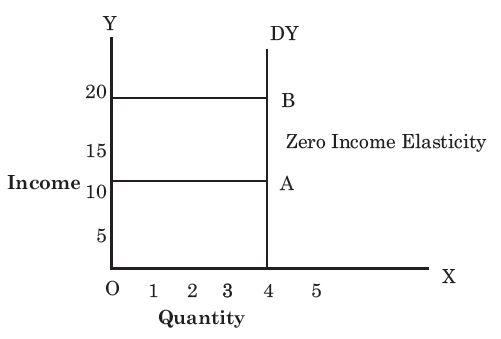
Fig: Zero Income elasticity
b) Negative income elasticity: A given increase in the consumer’s money income is followed by an actual fall in the quantity demanded of a commodity. This happens in the case of economically inferior goods (Ei < 0).

Fig: Negative income elasticity
c) Unitary income elasticity: A given proportionate rise in the consumer’s money income is accompanied by an equally proportionate rise in the quantity demanded of a commodity and vice versa (Ei=1).

Fig: Unitary income elasticity
d) Income elasticity of demand greater than unity: For a given proportionate rise in the consumer’s money income, there is a greater proportionate rise in the quantity demanded of a commodity. Ei is greater than unity. This is in case of luxuries.

Fig: Income elasticity of demand greater than unity
e) Income elasticity of demand less than unity: For a given proportionate rise in the consumer’s money income, there is a smaller proportionate rise in the quantity demanded of a commodity. The income elasticity of demand is less than unity in case of necessaries i.e., the percentage expenditure on necessaries increases in a smaller proportion when the consumer’s money income goes up (Ei < 1).

Fig: Income elasticity of demand less than unity
