– The key steps involved in determining whether a project is worthwhile or not are :
- a) calculate the costs and benefits of the project.
- b) Assess the riskiness of the project.
- c) calculate the cost of capital.
- d) Compute the criteria of merit and judge whether the project is good or bad.
– The important investment criteria are classified into two broad categories :-
- Discounting Criteria :-
– It takes into account of the time value of the money( calculate present value of future worth)
– It has mainly three popular methods:-
I) NPV
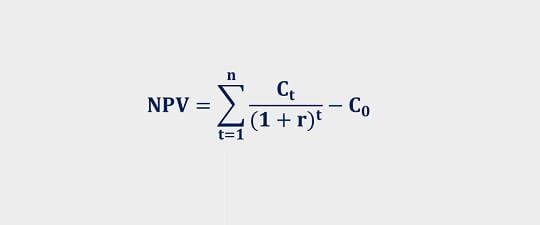
where ,
NPV > 0 , accept project
NPV < 0 , reject project
NPV = 0 , indifferent in decision making.
ii) B/C ratio or profitability index
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Profitability_Index_Oct_2020-011-3cc06137c4e24b7dbef3515c7d989bd3.jpg)
– It is the ratio of present worth of benefit stream divided by present worth of cost stream.
Where ,
B/C > 1 , project accepted
B/C < 1 , project rejected
B/C = 1 , Indifferent
iii) Internal rate of return ( IRR )
– Earning rate of project under evaluation.
– Discount rate at which NPV= 0 .
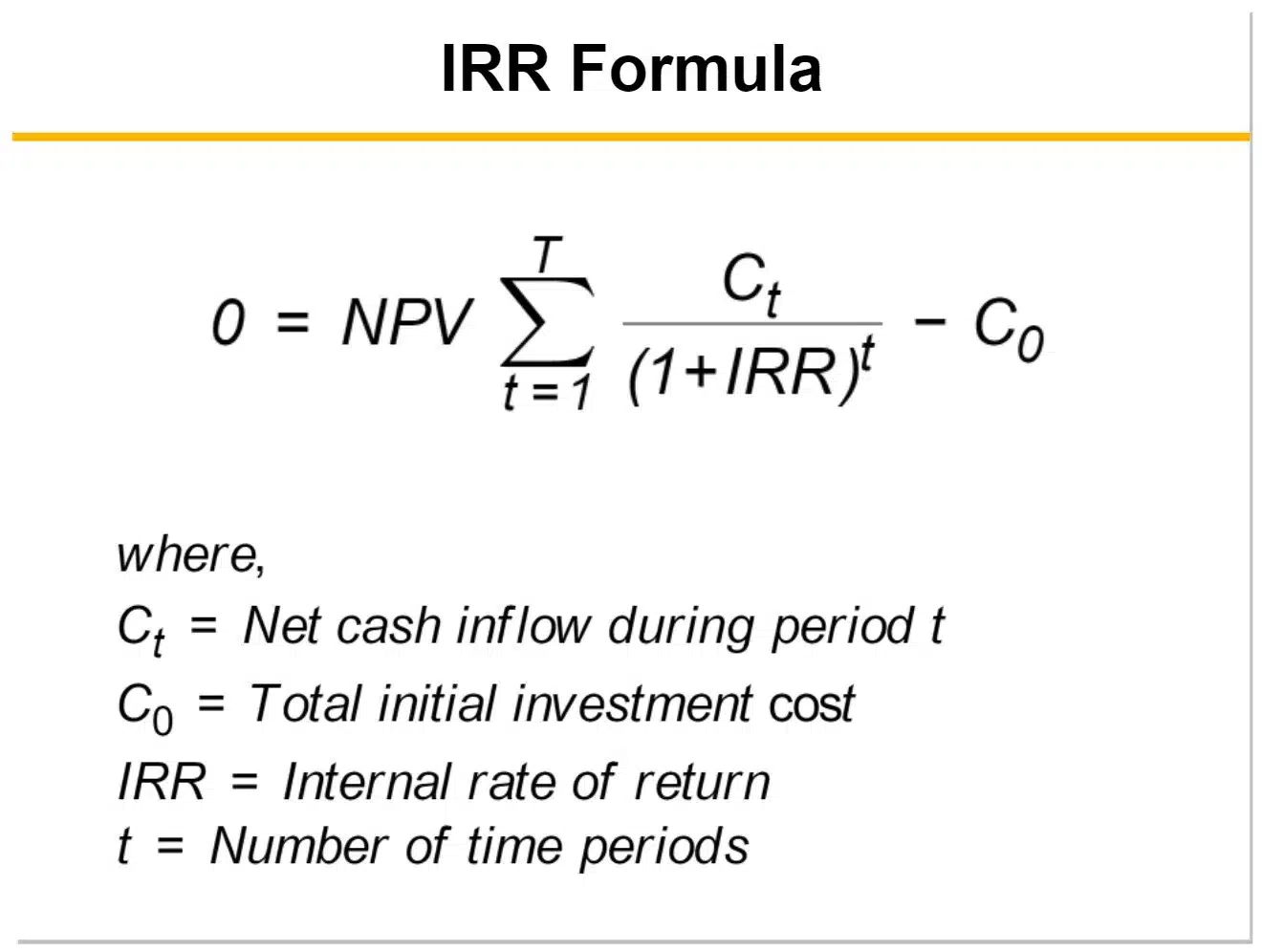
IRR > cost of capital , accept project.
IRR < Cost of capital , reject project.
- Non – discounting criteria :
I) Simple rate of return :
– Express average annual net income as % of the initial amount invested in the projet.
SRR = Y-D / I
where , Y = Average annual net income
D= Annual depreciation
I= Initial investment
SRR> required rate of return , project accepted.
ii) Pay back period :
– Length of time required to recover the initial investment .
Pay- back period = Initial investment / annual cash flow.
– Shorter the pay back period , project is beneficial , hence accepted.
Advantages :
a) Simple in both concept an evaluation.
b) Rough and ready method for dealing with the risk.
Limitations :
a) Fails to reconsider time value of money.
b) Ignores cash flow beyond pay back period.
Iii) Proceeds per unit of outlay :
Proceeds per unit of outlay = Total value of incremental production/ Total amount of investment
iv) Break even analysis :
– Point at which , company is neither at profit nor at loss.
