About Lesson
It may be defined as the ratio of proportionate change in the quantity demanded of a commodity to a given proportionate change in income of the consumer.
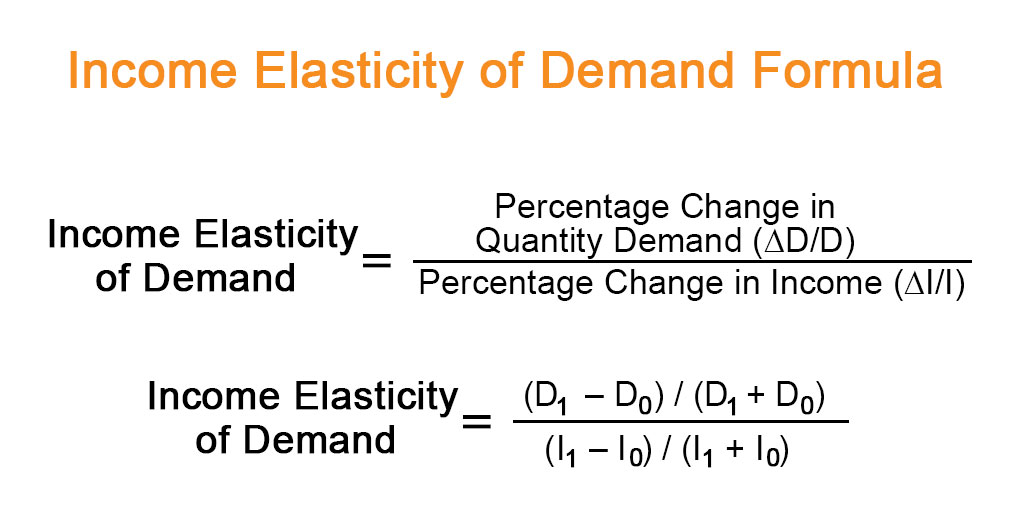
Fig: Equation of income elasticity
If, for instance, consumer’s income rises from Rs. 1000 to Rs. 1200, his purchase of the good X (say, rice) increases from 25 kgs per month to 28 kgs, then his income elasticity of demand for rice is:
Ei = (3/200) X (100/25) = 0.60
From this, we conclude that the quantity demanded of rice rises by 0.60 percent if the income of the consumer rises by one percent.
